Diabetes in pets is not a condition that exists in isolation. It touches nearly every aspect of daily life, from feeding schedules and medication timing to activity levels and emotional well-being. For senior pets especially, diabetes often arrives alongside age-related changes that make stability more important than ever. While modern veterinary medicine provides effective tools to manage diabetes, the most powerful element of long-term success is not a medication or device. It is routine.
Routine and consistency form the foundation of diabetic pet care. They reduce physiological stress, stabilize blood glucose levels, and give both pets and caregivers a predictable framework that supports healing rather than chaos. When routines are carefully established and thoughtfully maintained, diabetic pets can live comfortable, engaged lives well into their senior years.
Why Diabetes Responds So Strongly to Routine
Diabetes mellitus in pets involves impaired regulation of blood glucose, either because the body does not produce enough insulin or because it cannot use insulin effectively. This delicate balance is easily disrupted. Variations in food intake, medication timing, exercise, and stress can all influence glucose levels.
Routine creates predictability for the body. When meals, insulin, activity, and rest occur at consistent times, the pet’s metabolic system adapts to that rhythm. Hormones involved in digestion, energy use, and glucose uptake become more synchronized. Over time, this reduces sharp fluctuations that can lead to hypoglycemia or prolonged hyperglycemia.
For senior pets, this predictability becomes even more valuable. Aging bodies adapt more slowly, recover less efficiently from stress, and often tolerate change poorly. A stable routine acts as a buffer against these vulnerabilities.
Feeding Schedules as the Anchor of Diabetic Care
 Among all routine elements, feeding schedules are often the most critical. Meals directly affect blood glucose levels, and their timing must align with insulin administration when insulin is part of the treatment plan.
Among all routine elements, feeding schedules are often the most critical. Meals directly affect blood glucose levels, and their timing must align with insulin administration when insulin is part of the treatment plan.
Consistency in meal timing allows insulin to work as intended. When food arrives at expected intervals, glucose enters the bloodstream in a predictable pattern. This reduces sudden spikes and minimizes the risk of insulin acting without adequate glucose present.
Consistency also applies to portion size and food composition. Sudden changes in calorie intake or macronutrient balance can significantly alter glucose control. Even small deviations, such as frequent treats or unplanned snacks, can accumulate into measurable effects.
For caregivers, maintaining this consistency may require lifestyle adjustments. However, many find that once the routine becomes habitual, it reduces daily decision fatigue and anxiety. The pet learns when to expect meals, which often decreases food-related stress behaviors.
Insulin Timing and Medication Reliability
 When insulin or oral glucose-regulating medications are prescribed, timing becomes non-negotiable. These medications are designed to act within specific windows. Administering them too early, too late, or inconsistently can undermine their effectiveness.
When insulin or oral glucose-regulating medications are prescribed, timing becomes non-negotiable. These medications are designed to act within specific windows. Administering them too early, too late, or inconsistently can undermine their effectiveness.
Routine insulin timing supports stable glucose curves. It allows veterinarians to interpret monitoring data accurately and make informed dosage adjustments. Without consistency, glucose readings become difficult to interpret, increasing the risk of inappropriate dosing changes.
For senior pets, reliability is especially important. Age-related changes in kidney function, digestion, and circulation can already influence how medications are absorbed and utilized. Consistent timing reduces additional variables.
Many caregivers benefit from pairing medication administration with another fixed daily activity, such as feeding or morning walks. This habit stacking reinforces consistency and reduces the risk of missed doses.
Activity Patterns and Glucose Stability
Exercise plays an important role in glucose utilization. Physical activity helps muscles absorb glucose, often lowering blood sugar levels. While exercise is beneficial, inconsistency can create challenges.
Sudden increases in activity may cause unexpected drops in glucose, while periods of inactivity can contribute to elevated levels. Establishing a predictable activity pattern allows the body to anticipate energy demands.
For senior pets, activity routines should prioritize gentleness and regularity over intensity. Short, consistent walks or play sessions are often more beneficial than sporadic bursts of exertion. The goal is not to push physical limits but to support metabolic balance.
Routine activity also supports joint health, circulation, and mental engagement, all of which contribute to overall quality of life.
Stress Reduction Through Predictability
Stress has a measurable impact on blood glucose. When pets experience anxiety or uncertainty, stress hormones such as cortisol can raise glucose levels. Chronic stress may complicate diabetic management and increase insulin resistance.
Routine reduces stress by making the environment predictable. Pets thrive on knowing what comes next. When daily events follow a familiar pattern, the nervous system remains calmer.
Senior pets are particularly sensitive to environmental stressors. Changes in household schedules, noise levels, or caregiving routines can disrupt their sense of security. Consistency provides reassurance, helping them remain emotionally regulated.
This emotional stability is not separate from physical health. Calm pets often eat more reliably, rest more deeply, and tolerate medical care more easily.
Monitoring and Record-Keeping as Part of Routine
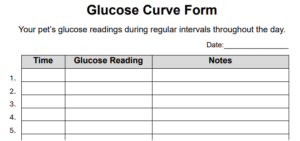 Monitoring blood glucose, observing appetite, tracking water intake, and noting behavior changes are all essential components of diabetic care. When these observations occur at consistent times, patterns become clearer.
Monitoring blood glucose, observing appetite, tracking water intake, and noting behavior changes are all essential components of diabetic care. When these observations occur at consistent times, patterns become clearer.
Routine monitoring allows caregivers to recognize subtle trends before they become emergencies. Changes in thirst, appetite, or energy levels are easier to detect against a stable baseline.
Keeping records reinforces routine for both the caregiver and the pet. Logs provide valuable information for veterinary appointments and help guide long-term management decisions.
For many caregivers, record-keeping initially feels burdensome. Over time, it often becomes a reassuring habit, offering a sense of control and understanding.
Routine and Cognitive Health in Senior Pets
Many senior pets experience cognitive changes similar to dementia in humans. These changes can include confusion, altered sleep patterns, and increased anxiety. Diabetes may exacerbate these symptoms by affecting brain glucose availability.
Routine supports cognitive function by reinforcing familiar patterns. Predictable schedules reduce confusion and help pets navigate their environment with confidence.
Feeding, medication, and activity routines act as anchors throughout the day. They provide structure that supports mental clarity and emotional comfort.
Caregivers often notice that senior diabetic pets with stable routines appear calmer and more engaged than those exposed to frequent changes.
Adapting Routine Without Losing Consistency
While consistency is essential, rigidity can become counterproductive. Life changes, health fluctuations, and aging itself may require adjustments.
The key is gradual change rather than abrupt disruption. When modifications are necessary, adjusting one element at a time allows the pet’s body to adapt without destabilizing glucose control.
Veterinary guidance is especially important during transitions. Changes in diet, insulin type, or activity level should be monitored closely to ensure safety.
Consistency does not mean refusing to evolve. It means maintaining predictability even as circumstances shift.
The Caregiver’s Role in Sustaining Routine
 Caring for a diabetic senior pet is a long-term commitment that extends beyond technical tasks. Caregivers provide emotional stability through their own consistency.
Caring for a diabetic senior pet is a long-term commitment that extends beyond technical tasks. Caregivers provide emotional stability through their own consistency.
Pets often mirror human behavior. Calm, confident caregivers help reinforce a sense of security. When routines are followed without stress or frustration, pets respond positively.
Caregivers also benefit from routine. Predictable schedules reduce anxiety, improve confidence, and make caregiving more sustainable over time.
Support systems matter. Shared calendars, reminders, and communication among household members help maintain consistency even when responsibilities shift.
When Routine Breaks Down
Despite best efforts, routines sometimes falter. Illness, travel, emergencies, or caregiver fatigue can disrupt schedules.
When disruptions occur, returning to routine as quickly as possible helps restore balance. Monitoring closely during these periods is essential.
Self-compassion is also important. Diabetic care is complex, and perfection is unrealistic. What matters most is commitment to consistency over time, not flawless execution every day.
Veterinary teams can provide guidance during challenging periods, helping caregivers recalibrate without judgment.
A Foundation for Long-Term Well-Being
Routine and consistency are not merely management tools. They are acts of care that honor the needs of diabetic and senior pets.
By creating predictable patterns in feeding, medication, activity, and monitoring, caregivers support the body’s natural rhythms. This stability reduces stress, improves glucose control, and enhances quality of life.
For senior pets living with diabetes, routine is more than habit. It is a language of safety, comfort, and trust. Through consistency, caregivers offer their pets not just longer lives, but better ones.